Glass Circular Broth Tube, For Chemical Laboratory at Rs 55/piece in

Broth Culturing YouTube
2.1: Introduction. 2.1.1: Video Introduction. 2.2: Aseptic Technique. 2.3: Using a bacto-Incinerator to Sterilize the Inoculating Loop. 2.4: Transferring the Inoculum into a Broth Tube. 2.5: Transferring the Inoculum into a Petri Plate. 2.6: Forms of Culture Media/Oxygen and Temperature Requirements. 2.7: Colony Morphology and Pigmentation.
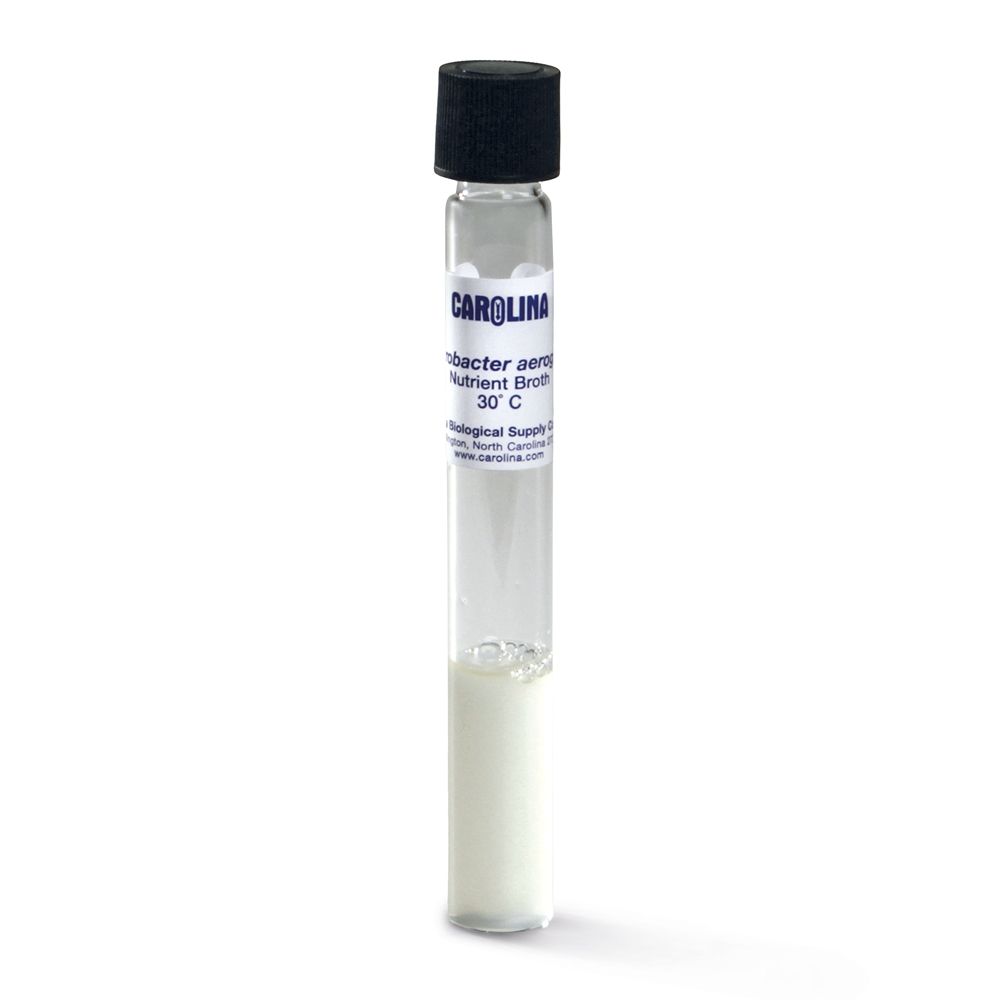

Enterobacter aerogenes, Living, Nutrient Broth, Tube Carolina
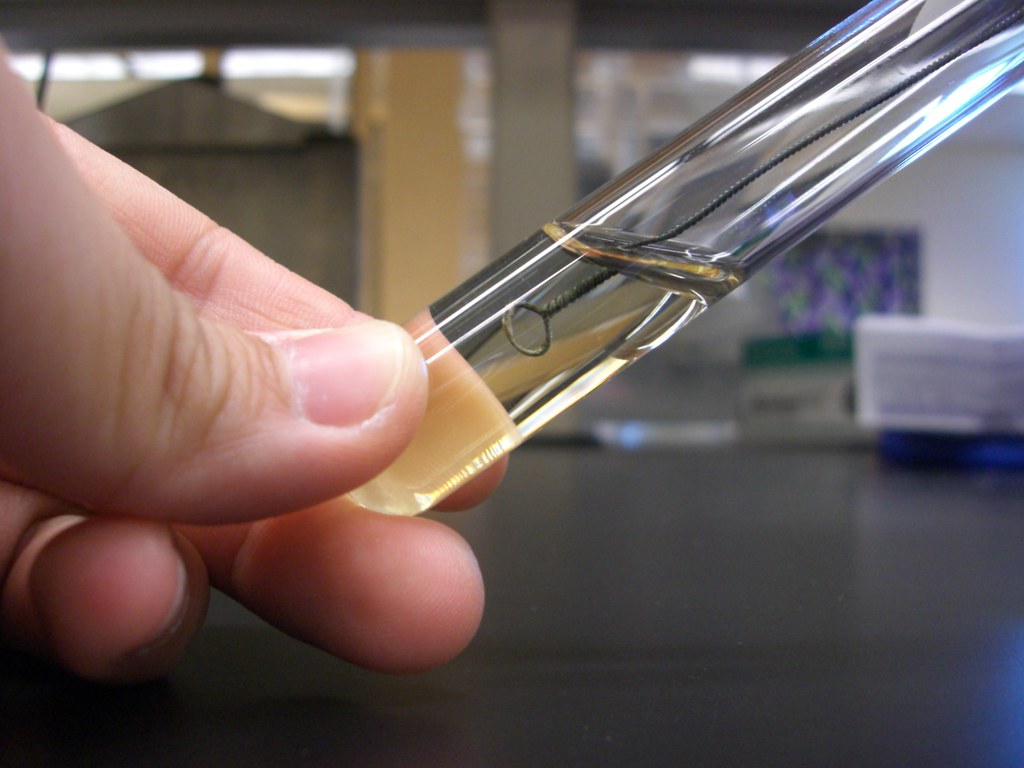
5. Holding the tube in your non-dominant hand, remove the cap of the bacterial culture with your little finger on your dominant hand. Dip the cotton end of the swab into the broth and then slightly press the swab against the inside of the tube to expel any excess broth. Recap the bacterial culture tube and place it in a test tube rack. 6.

Glass Circular Broth Tube, For Chemical Laboratory at Rs 55/piece in
This video lesson demonstrates proper aseptic technique for inoculating broth tubes, slant tubes, and stab tubes in a microbiology lab.
Medical Microbiology October 11
To confirm positive tubes, transfer one loopful from gas positive LST tubes to EC broth and incubate in a covered circulating waterbath at 44.5°±0.2°C for 24 ± 2 hr. Gas production in EC is a.
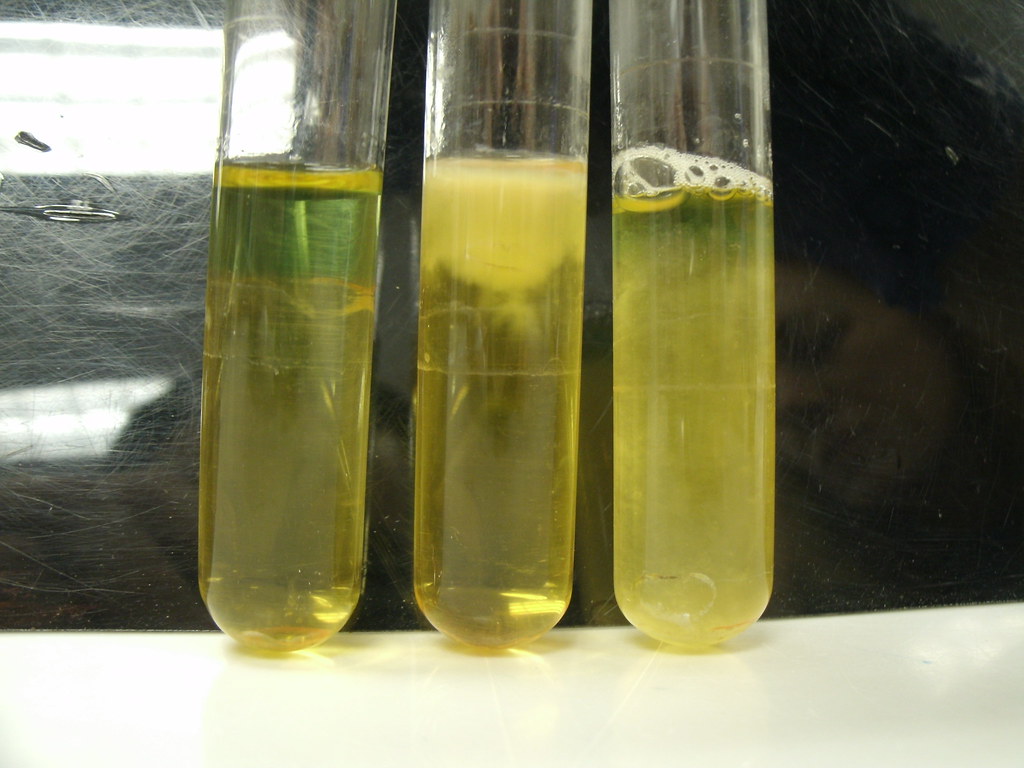

GE0203thioglycollate Thioglycollate broth (l to r) uninocu… Flickr
4. Now insert the loop into the E. coli broth culture and then remove it, carrying out a loopful of culture from the tube. See Figure 2. Replace the tube cap and return the tube to the storage rack. 5. Pick up and remove the cap from the tube of sterile Nutrient broth labeled "broth transfer" in the same manner as outlined in step 3a above. 6.

Edge Biologicals Dehydrated Culture Media Nutrient Broth Nutrient
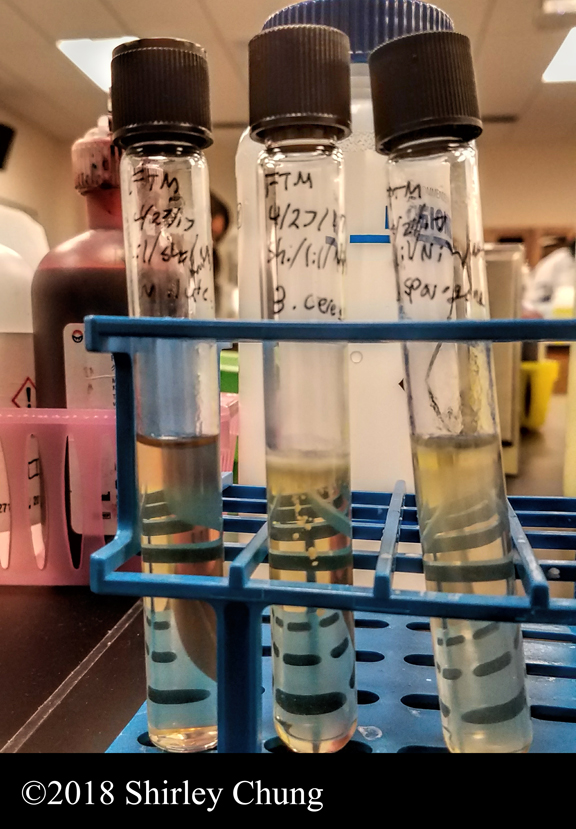
Broth tubes should be observed before disrupting or shaking, then assessed again after gently mixing the tube. One should also note any pigmentation. Turbid-many bacteria will form uniform turbidity (cloudiness) throughout the test tube. Sediment-bacteria may settle to the bottom of the test tube. The broth may be very clear or slightly turbid.
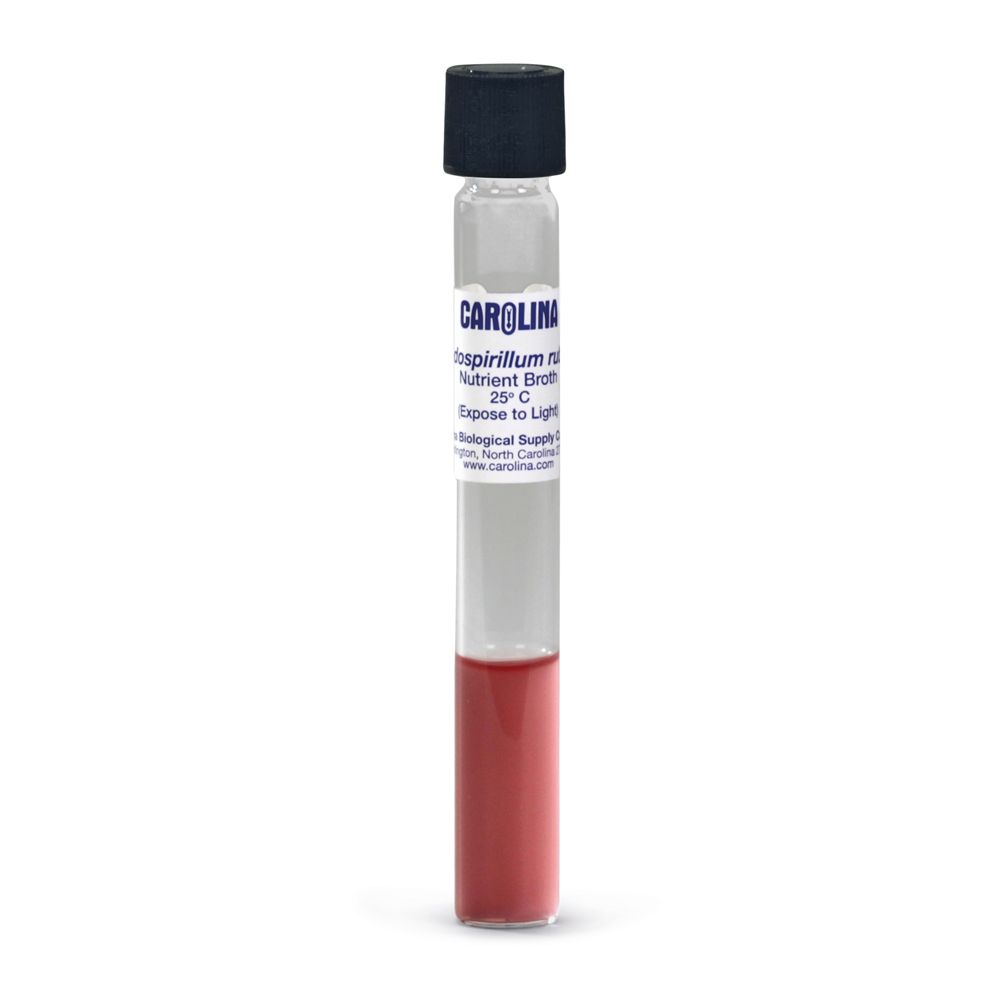

Rhodospirillum rubrum, Living, Nutrient Broth, Tube
Set the nutrient broth tube in the tube rack. 11. Using your non-dominant hand, remove the rubber stopper from the lyophilized S. marcescens culture vial. 12. Dispense 1 ml of tryptic soy broth into the lyophilized S. marcescens. Use the transfer pipette to stir the contents of the vial, breaking up the lyophilized pellet if needed.
Nutrient Broth, Prepared Media Tubes, Pack of 10 Carolina Biological
Liquid broth allows bacteria to grow at varying oxygen levels, since the oxygen available decreases as the depth of the broth increases. See the test tube diagram below for an illustration of the growth patterns of microbes with different oxygen requirements: Obligate aerobic bacteria, those that must have oxygen to extract energy from food.

Microbiology Broth tube. Basic Sciences
Broth Culture. Broth culture may sound delicious, but it would not be a great idea to drink it! This growth media is placed in broth tubes, allowing bacteria to grow inside, and gets its name from.

Public Domain Picture This is a thioglycollate broth culture of
Broth tubes. The only difference between broth and agar media is that broths do not contain an agar component. We use broth tubes primarily for specific assays, or (rarely) for bacteria that will not form colonies on a solid surface. In broth a species may display motility and/or a characteristic pattern of association among individual cells.

Broth Inoculation pt.2 1. Flame the entire length of the l… Flickr
Broth Subculture. Obtain 2 sterile glass culture tubes, a bottle of Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and a test tube rack. With small pieces of colored tape, label each tube with your name and either "S" for subculture, or "C" for control. Using aseptic technique, use a 10 ml graduated pipette to transfer 2 ml of broth to each tube.

Serratia marcescens, Living, Nutrient Broth, Tube Carolina Biological
Thioglycollate broth is the enrichment broth most frequently used in diagnostic bacteriology. This broth supports the growth of anaerobes, aerobes, microaerophilic, and fastidious microorganisms. It contains many nutritive factors, including casein, yeast, beef extracts, and vitamins to enhance the growth of the most medically important bacteria.

Selenite Broth
Aseptically inoculate one trypticase soy broth tube, one trypticase soy agar slant tube, one trypticase soy agar stab tube, and one trypticase soy agar plate with B. subtilis. Remember to label all tubes with a wax marker. When streaking the agar plates, this procedure is termed streaking for isolation and has a diluting effect. The friction of.

Brilliant Green Bile Broth (+ Durhams Tube), Universal Southern Group
Broth Subculture. Obtain 2 sterile glass culture tubes, a bottle of Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and a test tube rack. With small pieces of colored tape, label each tube with your name and either "S" for subculture, or "C" for control. Using aseptic technique, use a 10 ml graduated pipette to transfer 2 ml of broth to each tube.

Micrococcus luteus, Living, Nutrient Broth, Tube
Phenol Red Broth is a general-purpose differential test medium typically used to differentiate gram negative enteric bacteria. It contains peptone, phenol red (a pH indicator), a Durham tube, and one carbohydrate (glucose, lactose, or sucrose). Phenol red is a pH indicator which turns yellow below a pH of 6.8 and fuchsia above a pH of 7.4.

Phenol Red Broth Base Lactose with Durham Tube, Prepared Media Tubes
Using a sterile pipette tip or toothpick, select a single colony from your LB agar plate . Drop the tip or toothpick into the liquid LB + antibiotic and swirl. Loosely cover the culture with sterile aluminum foil or a cap that is not air tight. Incubate bacterial culture at 37°C for 12-18 hr in a shaking incubator.