Pollination of vegetable plants... do I need more than one?

Bees can detect Covid19 Exposing the Big Game
Many, but not all, crops are self-pollinating. This includes: beans), broccoli, cabbage, carrots, cauliflower, corn, kohlrabi, onions, and peppers. Fruit trees also self-pollinate including apples, cherries, peaches, and pears. If you're looking for a self-pollinating blackberry, blueberry, or raspberry plant, check out Bushel & Berry's.

Increase Your Harvest Using Your Own Hands
At this time of day, the blooms will be fully open and insect activity is at a minimum. To pollinate by hand, simply brush the inside of the male flower with a small paintbrush and then swab the inside of the female flower to transfer the pollen. To do the same thing without a paintbrush, just pick a male bloom, peel off its petals, and lightly.

Pollination
Grow Your Own: 10 Self-Pollinating Vegetables for Easy and Bountiful Harvests.Looking for self-pollinating vegetables that can thrive in your garden?Look no further! Discover the beauty of growing your own produce with these easy-to-grow, self-sufficient veggies. Say goodbye to the hassle of cross-pollination and hello to a bountiful harvest.Plus, they're perfect for beginner gardeners and a.
Smart Gardening Pollination in vegetable gardens and backyard fruit
What veggies do not need pollinators to produce: • All leafy greens. • Brassicas: broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage and kohlrabi. • Below ground root veggies and tubers such as carrots, parsnips, salsify, potatoes, sweet potatoes, horseradish. • Ground level root veggies such as beets, turnips, rutabagas. • Most legumes including peas.

Self Pollination Types, Advantages and Disadvantages
Twitter. Vegetables are pollinated in two ways: self-pollination and cross-pollination. Self-pollinators are plants that produce flowers that are usually fertilized by their own pollen, commonly when the male and female flower parts are contained within the same flower. Cross pollinators are plants with flowers that require pollen from another.

Pollination Pollination, Vegetables, Corn
Many legumes such as lima beans, garden beans, soybeans, peas and peanuts likewise largely self-pollinate. Often, pollen is shed onto the stigma while the flower is still closed, early in the morning before bees are present. So, bees aren't absolutely necessary, but… the flowers are still fertile and occasionally use the pollen brought by bees.

Learning About Pollination with Vegetables {Garden Blog Hop} The
Vegetable crops that produce a fruit (such as tomatoes and peas)require pollination in order to develop fruit. Pollination occurs when pollen from a flower's male sexual organ (stamen) comes into contact with a flower's female sexual organ (stigma). Self-pollinators (such as tomatoes and peas) have both male and female parts on the same flower. Wind or insects dislodge the pollen, which.

Hand Pollination In Vegetables.Full Guide. YouTube
Tomatoes and peppers self-pollinate, meaning each flower contains all the necessary plant parts to make a fruit. But many vine crops like zucchini produce different male and female flowers. The male flower will have pollen-laden stamens and the female flower will usually have what looks like the tiny bud of a vegetable at the base.

Plant for Pollinators Plant Something MA Plant Something MA
When to hand pollinate. If you have a non-self-pollinating vegetable, then first you need to keep an eye on when the male and female flowers are blooming. Male flowers generally grow on a straight stem. Female flowers often have a tiny baby vegetable at the base of the flower.

How to Know Which Fruits & Vegetables Need Pollinators Pollination
Quick facts. Tomatoes, peppers, beans and peas are good choices for seed saving. They have flowers that are self-pollinating and seeds that require little or no special treatment before storage. Seeds from biennial crops such as carrots or beets are harder to save since the plants need two growing seasons to set seed.

Crosspollination Definition, Mechanism, & Facts Britannica
Self-pollination is a form of pollination in which pollen from the same plant arrives at the stigma of a flower (in flowering plants) or at the ovule (in gymnosperms ). There are two types of self-pollination: in autogamy, pollen is transferred to the stigma of the same flower; in geitonogamy, pollen is transferred from the anther of one flower.

Pollination Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Some vegetables commonly found in gardens -- lettuces, peas, beans and tomatoes -- need only themselves to fruit and set seed because they self-pollinate. These plants do not require a carrier of pollen, such as bees or the wind. Saving the seeds from these plants allows gardeners to grow new plants nearly exactly like the parent plants.

Self Pollinating Plants For Your Veggie Garden You Should Grow
The cross-pollinated vegetables in Group 3 may either set seed from their own pollen (self-pollinated) or from pollen received from another plant (cross-pollinated). They can be divided into two sub-groups: (A) vegetables pollinated by air-borne pollen and (B) vegetables pollinated by insect-borne pollen.
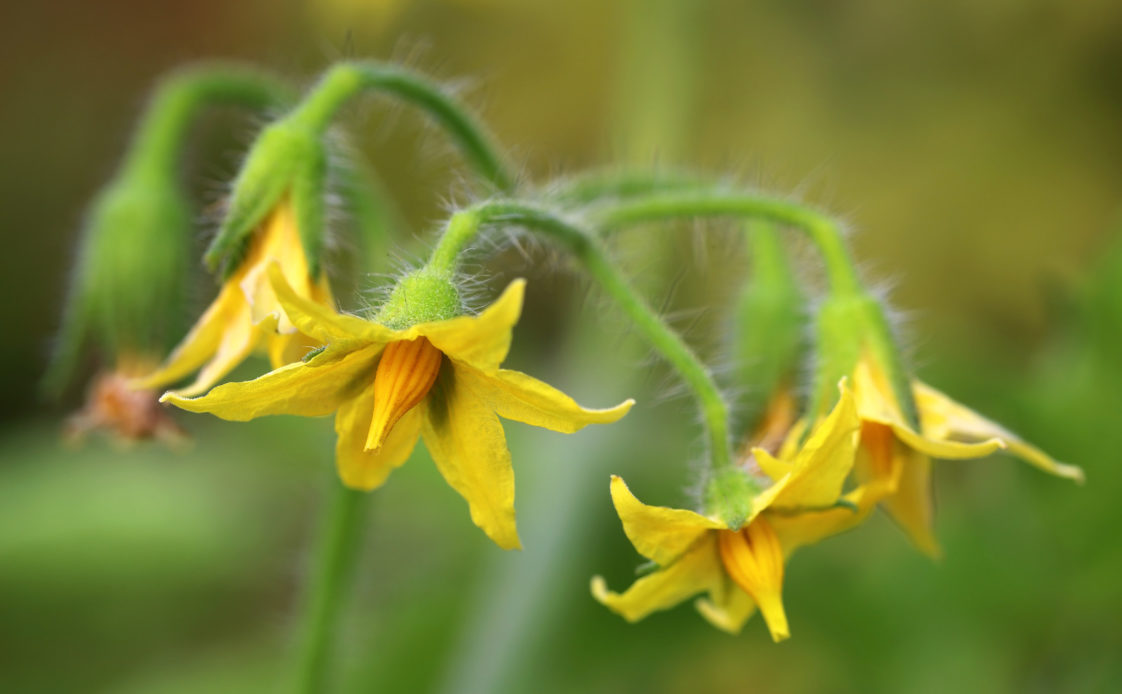

SelfPollinating Vegetables Harvest to Table
Self-Pollinating Legumes. Legumes, such as peas ( Pisum sativum ), lima beans ( Phaseolus limensis ), and green beans ( Phaseolus vulgaris ), including bush and climbing varieties, are self-pollinators. These vegetables grow well when sown directly in the ground as opposed to being started in a container indoors and then transplanted.

Pollination of vegetable plants... do I need more than one?
Self Pollinating Vegetables. Country Of Origin. Self Pollinating Cucumbers. Self Pollinating Tomatoes. Reimer seeds has over 5,000 quality vegetable, flower, and herb seeds for the home gardener and market growers. We do not sell any Genetically Modified seeds. This year we reduced our prices on many items, added new items, and have added.

A List of SelfPollinating Vegetables Hunker
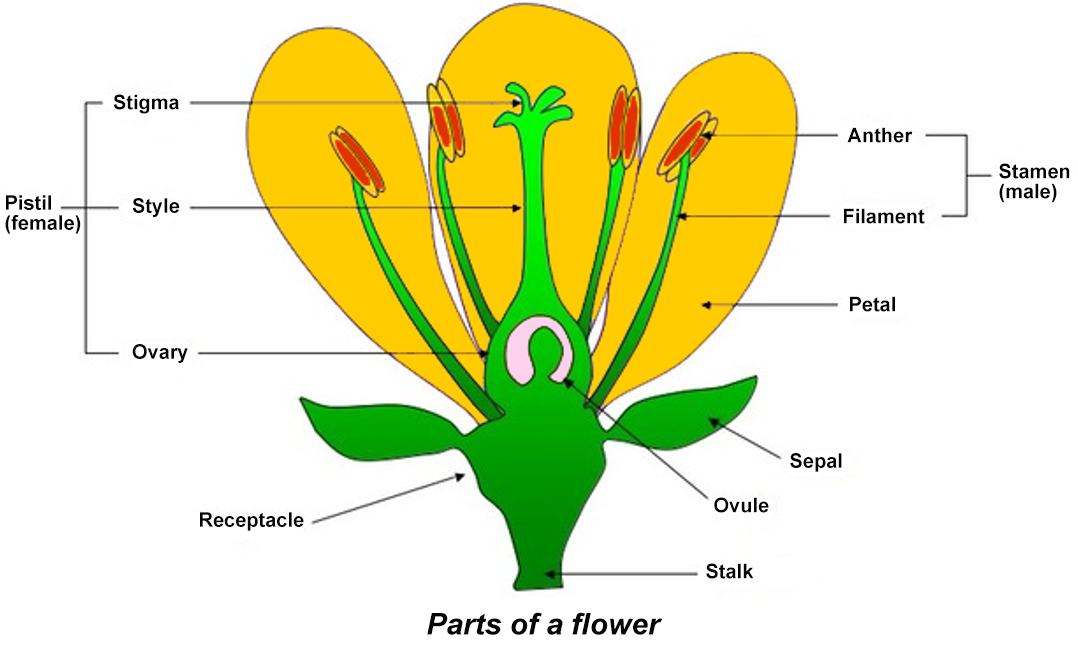
Pollination is the deposit of pollen grains from the anther (male structure) onto the pistil (female structure) of the same plant species (Fig. 1). Pollen can be transferred within an individual flower or between separate flowers. Successful pollination results in the production of viable seeds and a fruit to protect them.